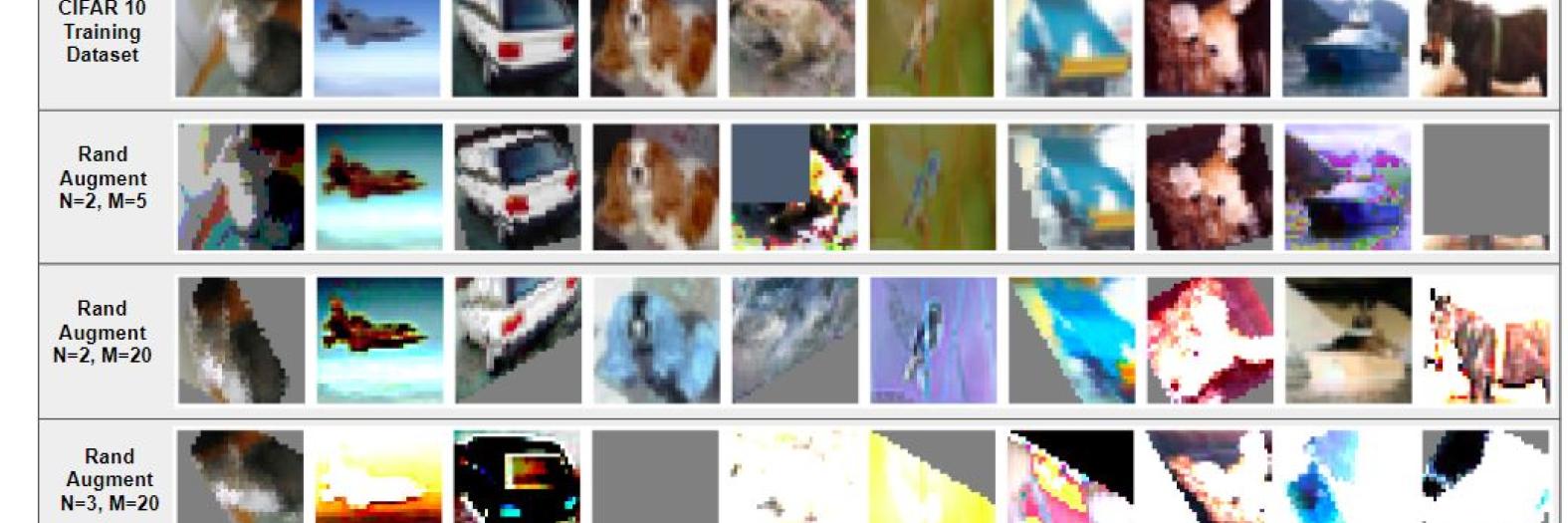
Targeting the distribution gap by data augmentation
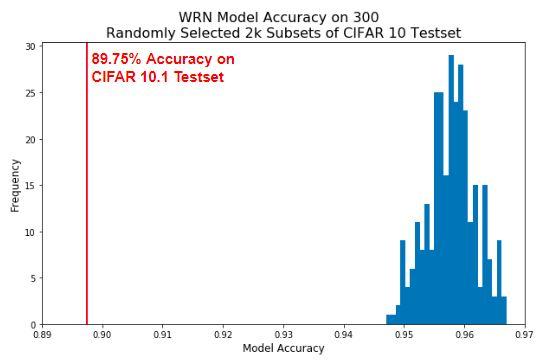
Computer vision algorithms suffer from a distribution gap when using common datasets, meaning that performance on a given dataset may not transfer over to a new one (i.e., CIFAR-10 to CIFAR-10.1). In this work, we explore using data augmentation as a means to lessen the distribution gap. Augmentation, using the RandAugment and CutMix methods, is used to create new datasets based off of CIFAR-10 and then used for training various models from literature. The models are then trained with a smaller learning rate for 50 epochs on the original CIFAR-10 data. Models are then evaluated on their performance on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-10.1 test sets, and the difference between these is the distribution gap. The augmentation method does not appear to provide any benefits for the distribution gap and worsens overall accuracy.