Stay Fit, Stay Safe
Problem Statement
The switch to remote work, lesser physical activities, and social isolation have created new challenges. With the increased level of stress and loss of jobs worldwide, the development of affordable, safe, and efficient ways to maintain mental and physical health has become more important. Yoga is a great way to achieve this. However, since the beginning of the pandemics, most fitness centers and yoga studios around the world have been either fully or partially unavailable and the practitioner’s ability to receive guidance from professional instructors has significantly reduced. The impacted population is vast: 36 million people in the US and approximately 300 million people around the world regularly practice yoga.
For most people, following prerecorded or live video lessons became the only viable alternative to in-person classes. According to Google query trends, the popularity of “yoga” search terms in YouTube queries has increased 2-3 times since March 2020. However, navigating the ocean of online sessions from fitness centers and independent instructors and finding a practice that fits one’s needs is challenging, especially for beginners, people with injuries, and those with hearing or vision disabilities. Currently, search on key phrases returns: “yoga” - about 338M results; “yoga video” - about 268M results; “yoga for beginners” - about 14.3M results; “yoga for low back pain” - about 2.3M results. Also, some essential parts of yoga practice, such as the participant's ability to choose areas of focus prior to the class and get warnings on conditions to avoid specific poses, became either hard or completely impossible.
How to improve the online yoga practice experience so that it retains its important advantages while becoming similar to the in-person practice in the areas where it is currently rated significantly worse? Solving this problem can help us find ways to enable millions of people around the world to stay physically and mentally fit while staying safe during the unprecedented times of the pandemic and beyond. To this end, we dedicated our capstone project in the Master of Information and Data Science to building AI tools that empower yoga practitioners to easily navigate online content and create personalized practice experiences in the safety of their homes.
Innovation
Based on interviewing yoga instructors and practitioners, we identified a high-priority need for augmenting the recordings of online yoga sessions with automatically generated summaries describing the exercise (time-based transcript in English and Sanskrit), interpreting the benefits for body and mind, and warning about contraindications. Such insights will open up a lot of further opportunities, such as enabling search and personalization of yoga practice based on the preferences entered by students, keeping track of individual progress, and helping to make the routine safe for all individuals.
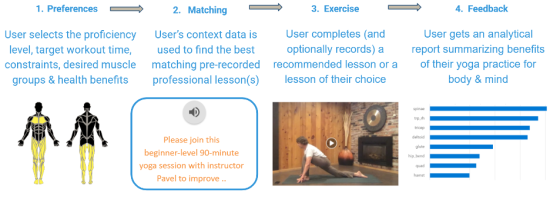
“Stay fit, stay safe” is an innovative deep learning AI solution deployed on the Azure cloud platform that elevates virtual yoga practice sessions by making online yoga experience more accessible to everyone in the world by making the video content searchable, providing the analysis of health benefits of the practice and personalized recommendations while reducing costs. It can be efficiently leveraged in numerous highly effective educational and self-development programs. The attached picture depicts the primary user story we address in the project. It incorporates a user-friendly UI, with a recommendation engine running behind the scene, allowing the yoga practitioner to specify their preferences and get personalized advice based on their current search criteria, prior history of exercise, and configured preferences:
To make it possible, we developed an on-demand service with a capability for multi-modal video summarization powered by computer vision AI. As part of the MIDS capstone project, we created a deep learning classifier for the detection of 72 main yoga poses. The classifier was trained and tested on over 14k images collected from open-source datasets and augmented with frames of poses contributed by project participants. We invested significant effort in providing privacy guarantees. The best model achieved an 87% accuracy score.
Yoga instructors provided us with access to over 100 hours of video lessons. We built an asynchronous pipeline that produces video summaries. Below is an example of an automatically generated annotation in natural language:
Please join this beginner-level 90-minute yoga session with instructor Pavel to improve the state of your body and mind. Primary health benefits of this practice include (but are not limited to) helping with insomnia, sciatica, depression, asthma, anxiety. The main focus of this session is on the following muscle groups: spinal extension, deltoid, glute, quad, triceps.
A yoga practitioner can use such a summary to help them design their practice and yoga curriculum for optimal health benefits. For more detailed insights, they can look into deep analytics for each video with a breakdown of the amount of time spent on each muscle group and health condition, the complexity of the exercise as a whole, and contraindications of individual poses. To provide accessibility for people with disabilities, the summaries are delivered in three modalities: text, audio (with the help of an automatic text-to-speech generator), and graphics.