RECO: Recovery Companion
Problem and Motivation
One in 33 Americans suffer from heart failure. Approximately 25% of heart failure patients are readmitted within 30 days of hospital discharge, costing the healthcare system billions annually. This issue is exacerbated by resource constraints and the limitations of form-based methods for monitoring patients post discharge. RECO aims to address these challenges by providing continuous, generative AI-driven monitoring and support for heart failure patients after hospital discharge. This solution aims to ensure better continuity of care and reduce readmission rates by enabling timely interventions.
Our Solution
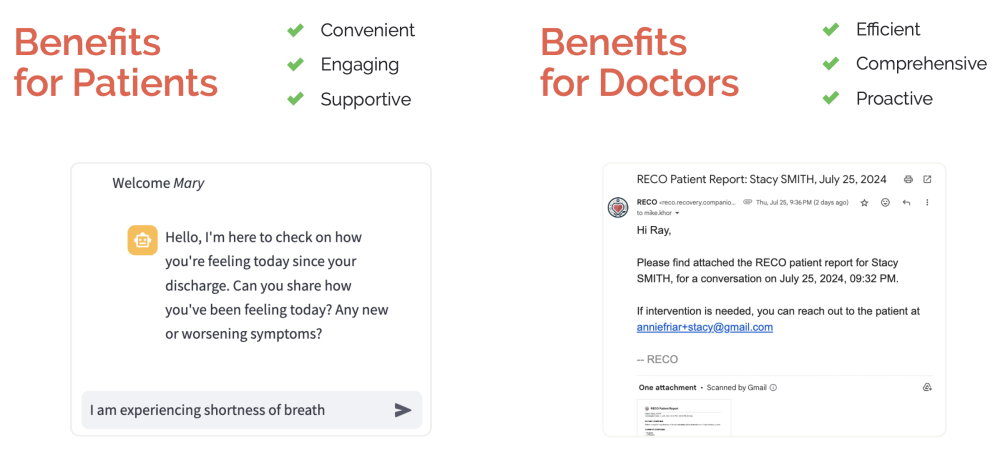
RECO aims to reduce readmission rates by providing continuous, AI-driven monitoring and support for heart failure patients. It collects clinically relevant patient health information, and then compiles this information into a structured report for their physician.
Data Source & Data Science Approach
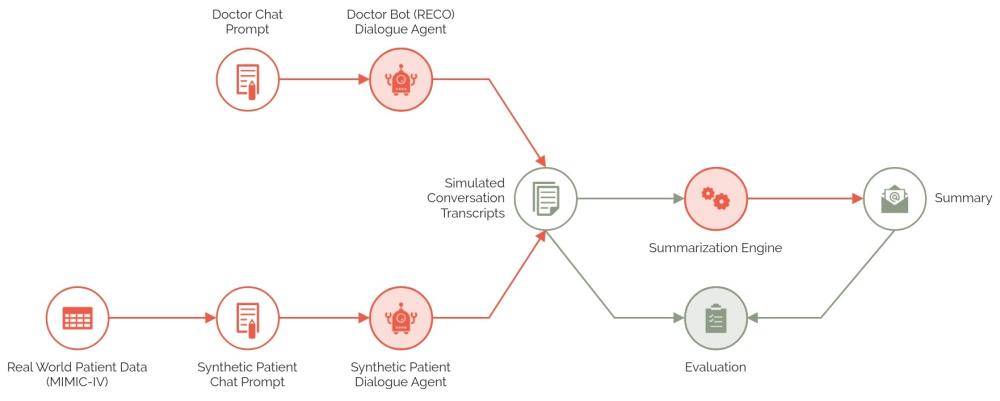
The RECO chatbot acts as a virtual doctor designed to monitor vital signs, medication adherence, and symptom progression. A synthetic patient bot represents a RECO patient, utilizing real-world, anonymized data from MIMIC-IV to simulate heart failure cases. These two bots engage in simulated dialogues to facilitate evaluation. Transcripts from the RECO chatbot’s interactions with patients are then summarized using a summarization engine, providing healthcare providers with easily digestible PDF reports.
Evaluation & Improvement
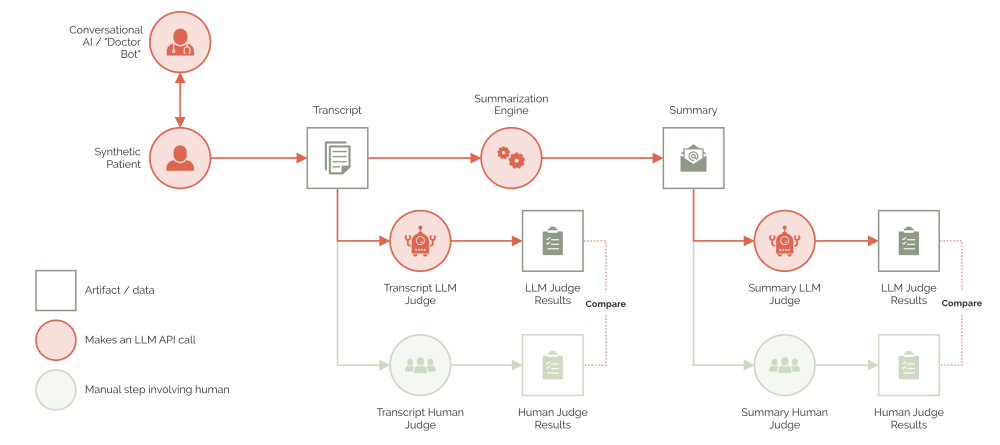
RECO’s performance is evaluated using a combination of synthetic patient profiles, LLM-as-a-judge, and human judges. First, we simulate conversations between our RECO chatbot and synthetic patients with various medical profiles and personas. Next, the conversation transcript is evaluated by LLM-as-a-judge, using key performance indicators such as dialog quality and RECO's ability to ask for relevant information from patients. To ensure the reliability of LLM-as-a-judge, we compared its outputs to the ground truth of human judgment and improved the LLM judge until it met the human standard. Once the automated evaluation pipeline was established, we were able to iteratively improve RECO’s performance.
Benefits of RECO
RECO addresses key challenges in post-discharge heart failure management by providing:
- Improved Data Accuracy: The summarization engine minimizes human error and provides consistent, relevant information for healthcare providers.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Doctors receive concise summaries, facilitating quicker and better-informed clinical decisions.
- Scalability: The system allows for the management of larger patient volumes without overburdening healthcare providers.
- Patient Engagement: Feedback indicates patients find the chatbot easier and more straightforward than traditional forms.
Key Learnings & Project Impact
RECO showcases several innovations in the development of AI-powered healthcare tools, including:
- Realistic Synthetic Patients: We generated high-quality synthetic patients using de-identified real-world data, enabling safe experimentation without compromising privacy.
- Scalable Evaluation Framework: We developed a scalable method for evaluating RECO, enabling rapid iteration and a higher-quality product.
- Clinically Informed End-to-End Solution: We created an end-to-end solution grounded in clinical expertise of heart failure and challenges of its management
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank our course instructors (Professors Joyce Schen, Zona Kostic), the UC Berkeley School of Information, and all those who provided invaluable feedback and support throughout the project.